This was originally published on The Success Bug website by Ashlyn Rosario.
We’ve all had amazing business startup ideas at some point in our lives.
Let’s say you had a brilliant idea for an ice cream business, featuring ice cream that stays frozen longer, or a killer idea about a way to simplify the job searching process. Excited, you run to your computer and start jotting down the idea. The thought almost seems to make too much sense. So, why doesn’t it work out?
Because no matter what your business startup ideas are, you need to develop a strategic, written plan for them.
The perfect method for developing a strategic business plan is called the Business Model Canvas. This business plan cheat-sheet features nine segment blocks essential for understanding your target consumers, how to reach them, what channels to use, and how to generate sales.
Here is an image of the Business Model Canvas. We recommend printing this out, so you can quickly add to it using a pen or pencil:
The right side of the business model canvas focuses on the customer, while the left side focuses more on the business itself.
You can download the official Business Model Canvas here.
Now, the BMC might look a bit confusing at first but bear with me. Because we’re going to break down every segment of the most effective ways you can use the Business Model Canvas to bring your startup ideas to life. Let’s get started.
1. Customer Segments + Value Proposition for Startup Ideas

When beginning the canvas for your business startup ideas, you’ll need to start with either the Customer Segment or Value Proposition component.
Why? Because the first two questions you need to ask yourself when creating a startup are “Who are the people that will buy my product?” and “What value can I add with my product?” For our breakdown today, we’re going to start with customer segments.
Customer Segments
When analyzing your potential customers and specifying your target market, here is a list of consumer types to focus on:
- Payers: People who pay a bill for your product or service
- End Users: People who will actually use your product
- Subsidized Users: People who will benefit from your product
- Influencers: People who have the power to affect the purchase of your product
- Decision Makers: People who may be responsible for business expansion, investments or company acquisition
Understanding the different types of customers your company might have is critical to creating a successful business. Once you know this, you can start to brainstorm different ways to attack each group.
Value Proposition
Now that you have a solid understanding of the different types of consumers you might have, you need to think about the kinds of value you can provide.
A value proposition is exactly what it sounds like: a promise of value to be delivered, communicated, and acknowledged. Now, don’t worry. We’re not here to tell you what type of business to start; this is simply a list of the different types of value propositions your business can offer.
- Gain Creator: businesses that benefit their customers in different ways, such as creating positive emotions, providing high functionality, or creating social gains
- Problem Solver: businesses that develop a course of action for fixing an identifiable problem such as lowering personal costs and keeps existing customers
- Pain Reliever: Describes how your product or service solves specific problems for customers
Having a basic understanding of Customer Segments and Value Propositions is the first step to get your startup ideas moving with the business model canvas. Filling this out as the first step will give you the foundation to be able to understand the rest of the grid. Which brings us to our next component…
2. Customer Relationships + Channels

Now that you have an idea of the types of customers valuable to your business and value propositions, you need to decide what channels to use. A channel refers to the different methods that businesses use to communicate and reach their customers. Confused? Here are some examples of sales channels.
- Wholesaler: A person or company that buys a large number of products from vendors and resells them to retailers.
- Retailer: A company that buys products from wholesalers or manufacturers and resells them to customers.
- Distributor: A person or business that sells goods or services to customers or end-users
- The Internet: A platform that companies can use to advertise their products and make a sale on.
There are multiple channels to sell your product. However, think about how much of your product you want to create and which channels work best with it.
Customer relationships and channels are the meat and potatoes of any successful business. With the BMC, you’ll know why it’s essential to make lasting relationships with your customer base and the different ways to reach them. Ultimately, the relationship you have with customers, whether personal, professional, or automated, will directly affect your business’s outcome. So, take some time with this step and be sure to think about what type of customer relationship you want to make through your company.
3. Revenue Streams for Startup Ideas

The Revenue Stream portion of the Business Model Canvas should be the bread and butter of your startup ideas. Why? Because the goal of every business is not only to retain customers but to make a profit. And you can do that by asking yourself these three vital questions when filling out the revenue stream section of the Business Model Canvas:
- How will the business make revenue?
- What is the business’s target audience?
- Through what method will the company will generate revenue? i.e., (subscription service, brick, and mortar, or online store.)
Understanding how the business will make revenue will allow you to avoid wasting time in unproductive areas. The general rule of thumb for your business startup ideas is to have between two to five avenues of revenue generation.
If you’re having trouble brainstorming ideas of what to fill in for this section, we’ve provided a few different popular areas of revenue generation below.
Examples of Revenue Generation Areas
- Service Revenue: Revenue is generated by providing service to customers and calculated based on time. For example, the number of hours of services provided
- Transactional Revenue: Proceeds from sales or goods that are (usually) one-time payments
- Project Revenue: Revenue earned through one-time projects with new or existing customers
- Recurring Revenue: This is one of the most popular areas of revenue generation: the proceeds from recurring payments for ongoing services to customers. This revenue model is so popular because it is transparent and creates a consistent flow of revenue for the business. Examples of companies that utilize this business model are Netflix, Disney+, Hulu, and Spotify
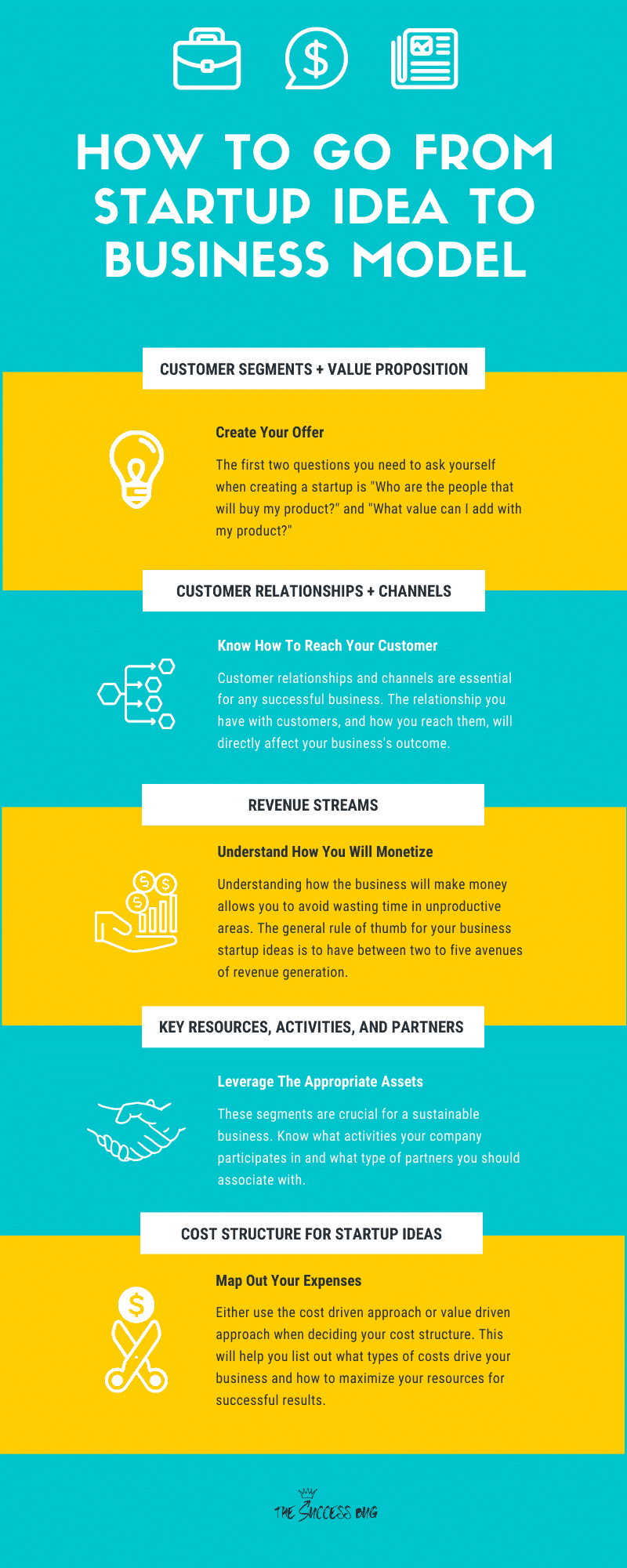
4. Key Resources, Activities, and Partners for Startup Ideas
These components refer to the “front stage” of the Business Model Canvas. They’re crucial ingredients for sustaining business, what activities companies participate in, and what type of partners and relationships they develop with other companies and non-consumers.
Key Resources
Key resources are considered the “assets” of your company, which are vital for sustaining and supporting your business. They also allow you to create a compelling value proposition more easily. Examples of key resources include physical resources, human resources, intellectual resources, and financial resources.
The 4 Types of Key Resources for Startup Ideas
- Physical resources: These include physical goods like raw goods, buildings, vehicles, machines, etc.
- Intellectual Resources: These include goods that come from the mind, like proprietary knowledge, patents, partnerships, etc.
- Human resources: These include human qualities like creativity, experience, organizational abilities, etc.
- Financial resources: These include commercial entities like cash, credit, stock, etc.
Key Activities
Key activities can vary depending on the type of business model companies use. These activities are categorized by production, which incorporates four design-related activities. These include manufacturing and delivering a product, problem-solving activities, platform, or networking activities.
Key Partners
Key partners are the network of suppliers, businesses, or nonconsumers that enable businesses to work. These can be the relationships that your company has with suppliers, business partners, and more.
These relationships are vital to the success of a business and will help your business succeed in areas that you may not be an expert in yourself. Now, there are four types of partnerships you can create.
The 4 Types of Key Partnerships for Startup Ideas
- “Coopetition”: This refers to a strategic partnership between you and a competitor. At first, this might sound like “flirting with the enemy.” But a “coopetition” is actually an effective way to create a more extensive user base for both you and your competitor. You know the old saying, “Keep your friends close and your enemies closer.” Well, when it comes to your startup ideas, this certainly applies.
- Buyer-Supplier: This is precisely what it sounds like: building a relationship with a buyer or supplier. Creating an element of trust between these two will create social proof for your business.
- Joint Ventures: Sometimes, joining forces altogether with a business that offers a similar service can be beneficial. A common example of this is when major law firms merge, often creating new opportunities for both businesses to increase their clientele. *Note* Not to be confused with a “coopetition,” a strategic partnership between your business and a competitor.
- Non-Competitors: This happens when you and a company you have no direct competition with partner up in a way that will benefit both parties. Here’s a wildly extreme example: Amazon. When Amazon purchased Whole Foods, the eCommerce giant entered the grocery industry overnight.
5. Cost Structure for Startup Ideas

If key resources, activities, and partners are “the front stage,” then Cost Structure is “the backstage” of the Business model canvas. It describes all of the costs incurred as a result of running your business.
Understanding the cost structure of your business startup ideas will allow you to pivot or persevere while running your business. Now, there are two components of cost structures.
The 2 Components of Cost Structure
- Cost-driven: This is the act of minimizing your costs as a business to give you an advantage over your competitors. Examples of companies that utilize this method are TJ Maxx, Marshall’s Walmart, or any store that provides value at lower prices.
- Value-driven: This type of cost structure focuses more on the design and overall maintenance of a product or service. When using a value-driven cost structure, your goal is to provide as much value with the product itself as possible. For example, Apple sells its products at a premium price but can justify it for its premium features.
Still having trouble deciding which cost structure to use? Here are some questions to ask yourself when considering each method:
- What key resources or key activities cost the most?
- What costs are the most important in my business model canvas?
- Is my business fueled by cost or value?
Asking yourself these questions will allow you to decide which cost-structure to use in no time. If you’re still struggling, another helpful way to determine what method to use is taking a look at your possible competitors and identifying which cost-structures they use. Then, you’ll be able to compare and find out whether or not their methods would suit your business as well.
Key Takeaways
It is vital to develop an organized business plan to map out strategic ways to deliver value to your customers when it comes to business startup ideas. The Business Model Canvas makes it easier for people to organize their business ideas in an organized way. When starting, you need to begin with either the customer segment or value proposition portions to assess your business’ scalability and how you can create and keep customers.
Next is choosing which channels to use in selling your product. Also, once you have customers, maintaining positive relationships with customers with excellent customer service practices is essential.
The Business Model Canvas helps to plan revenue stream methodologies such as deciding whether to use a subscription-based service or selling your products through a brick and mortar business model.
Finally, cost structures list out what types of costs drive your business and how to maximize your resources for successful results.
Planning on utilizing the BMC for your startup ideas? Let us know how in the comments below! If you enjoyed this article, you’ll love, “3 Things To Consider Before Starting Your Business!”